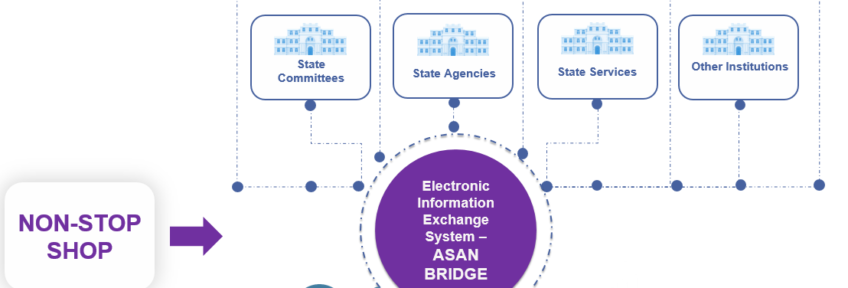
The E-Gov Development Center has developed a new information exchange tool named ASAN Bridge in order to enable government organizations to transfer the necessary data to each other in more stable, secure and prompt ways. Through the assistance of this system, the key development challenge in the country was addressed by simply enhancing the safety and efficiency of the procedures and serving citizens better.
Innovation Summary
Innovation Overview
The concept of digital and modern government requires effective management of large amounts of data. Prior to the development of the ASAN Bridge System, each government agency managed its own data and individually responded to citizen public service inquiries. However, in order to ensure a competent “non-stop shop” model of digital government services (fully digitized and proactive) and to provide better services to the citizens, various agencies have the obligation to transfer the crucial information in a safe and quick manner.
Taking into account the emerged need for such an information exchange tool, the ASAN Bridge System was created so as to deliver the required interoperability between government structures. ASAN Bridge System, as an integrated module of the e-Government Information System, provides coordination of government information resources and systems, as well as stable and secure exchange of information between those resources and systems. In this regard, the ASAN Bridge System brought about the needed change in the public sector as it altered and facilitated the existing procedures, and improved the performance of government organizations in terms of public service delivery.
Before building the ASAN Bridge System, the Azerbaijani government applied the leading example of the X-Road system developed by Estonia in 2001. Afterwards, based on the lessons and experience learned throughout the implementation process, a more developed system - ASAN Bridge project was created in compliance with the needs and requirements of the country. The major aim of the ASAN Bridge project is to provide secure, prompt and effective data exchange between government entities. The system was established using the open source components and does not depend on any physical equipment. The tools for carrying out the project are specified below:
- MS SQL, MongoDB, REDİS;
- Java (Spring Framework), Golang, JavaScript (Angular), Python
- Message queues: RabbitMQ
The ASAN Bridge System operates on a fully-functional basis for the best interest of the government and citizens. As a consequence of successful operations, today, 54 government organizations are part of the ASAN Bridge System, while 6 public entities consented to be integrated into the system. Currently, the negotiations with 12 governmental structures proceed so as to ensure full incorporation of all government agencies into the project as well as more efficient service delivery for the population. It should also be emphasized that delivery of the updated system named “ASAN Bridge 2.0” is expected by the end of 2022. The updated version will function on a larger scale and procure an improved degree of security.
Innovation Description
What Makes Your Project Innovative?
The utilization of ASAN Bridge System proved to be more effective, in the sense that it eliminated the complexities and slow procedures existent in the traditional service delivery. The system addressed the shortcomings of the traditional practices by hindering the misuse of the data and ensuring security. Further positive aspects of using ASAN Bridge :
- Not dependent on physical equipment (card, token, etc.);
- Ability to work on all Operating Systems (OS);
- Timely detection and prompt elimination of any problems within the system through the monitoring module;
- Relevant permissions can be managed centrally while transferring information from one institution to another;
- Acceptance and transfer of all types of services (XML, JSON, SOAP, Restful);
- Versioning of services in order to increase the sustainability of transmitted services;
- The services can be divided into sub-services, and thus transfer only the necessary information from the transmitted data to the other party.
What is the current status of your innovation?
The ASAN Bridge project demonstrated huge success and attracted the majority of the government agencies into the process. As a convincing proof, the ASAN Bridge System became the winner of the World Summit on the Information Society (WSIS) awards organized by International Telecommunication Union (ITU) in 2022. In the competition, which was held in 18 categories, ASAN Bridge presented by Azerbaijan became one of the first 5 projects that received the highest number of votes in the category “Building trust and security in the application of ICT” and was awarded as a champion project.
Given all these factors, the ASAN Bridge System is at the stage of diffusing lessons. The project was implemented successfully and the experience as well as the knowledge gained from this process is being shared with the public organizations of other countries. Apart from this, the system is being improved constantly by the project team and the updated version will be available in the upcoming months.
Innovation Development
Collaborations & Partnerships
Throughout the project, the majority of the public organizations in the country were attracted into the project as collaborators. The organizations provided the project team with the needed citizen-related as well as the operational data, Eventually, this cooperation assisted to coordinate all the resources and information from the database of government organizations which was critical for the creation of the ASAN Bridge System.
Users, Stakeholders & Beneficiaries
Since ASAN Bridge integrated all government entities into a single system, exchange of the data and rendering public services became a simplified task for the public employees. As a result of the innovated system, the public services became fast-paced, secure and more accessible to the citizens.
Innovation Reflections
Results, Outcomes & Impacts
The results of the project:
- 54 government entities were integrated into the system;
- 426 root services are offered;
- Over 218 billion transactions were realized.
The overall impact of the project:
- During the decision-making process, public officials can use state database within their mandate,
- To perform business operations, companies can make use of the information in the state database within the mandate.
The Monitoring and Evaluation team employed following techniques to measure the results and impact of the project:
- Interviews with the beneficiaries - Evaluation of the new system, satisfaction level and feedback about the rate of the effectiveness
- Evaluation Surveys - Assessing the quality of the trainings for learning new system, new public service delivery, and coordination
- Statistics related to the project results
Expected results and impact of the project:
- Reducing paper waste
- Decreasing queue in public and private entities
Challenges and Failures
Applying and adapting to the progress comes with its challenges. In the case of ASAN Bridge, the lack of relevant skilled staff and resistance to the progress by some workers generated obstacles throughout the implementation process. Given specific infrastructure requirements for the ASAN Bridge System, it was necessary to work with the employees who were aware of the modes of operation. Therefore, the following measures have been taken:
- Awareness and capacity-building activities for the staff of government institutions
- Advising and supporting the recruitment of skilled employees
Moreover, the existence of non-digital government structures posed a great challenge during this process. Eventually, we have been able to digitize the organizations through integration into the system. For this purpose, modernization of IT infrastructure was carried out.
Conditions for Success
The following measures were critical factors that led to the success of the ASAN Bridge System:
- Effective leadership and guidance - Experienced project managers and professionals were key to successful project completion.
- Proper communication between numerous state institutions - The usage of both formal and informal communication were ensured.
- Creation of the infrastructure to support information sharing - Generating the groundwork needed to alter the traditional service delivery methods was crucial in our case.
- Extensive monitoring and evaluation - Evaluating the results on a constant basis and checking the project progress were an integral part of the process.
Replication
Considering the infrastructure and resources employed for the creation of the ASAN Bridge System, the project is replicable, and can act as a useful example for other countries targeting digital transformation. Since the ASAN Bridge System encompasses the majority of the public organizations in Azerbaijan, the replicability of the project is plausible for the public entities out of the country.
For this reason, E-Gov Development Center signs Memorandum of Understanding with the governments who are in need of the exchange of experience and provides consulting so as to build the same system. The consultations cover the comprehensive analysis of organizational, financial and political aspects along with the technical elements. Currently, the implementation process for the beneficiary countries proceed with the help of these consultations.
Lessons Learned
In order to make needed adjustments and improvements, the following list of lessons were used as the reference points:
- During the implementation process, it was observed that the constant requests of government organizations led to the problem as the responsibility of each employee was not clarified and the requests were not directed to the particular accountable project member. For the purpose of addressing the issue, division of the workload and accountability area of every worker were specified, and the public organizations were informed accordingly.
- Another problem was the resignation of the project members, causing unawareness of the subsequent employee about the previous operations. For handling this problem, the new requirement of writing down all the operations was put into force.
Status:
- Diffusing Lessons - using what was learnt to inform other projects and understanding how the innovation can be applied in other ways
Date Published:
26 January 2023