As the overuse and misuse of narcotics pose a global public health threat, the Korean governance has developed a smart, digitalized real-time monitoring system for narcotics safety management. By utilizing this state-of-the-art technology, the government can analyze prescriptions, track patterns, and alert doctors to prevent the overuse and misuse of narcotics.
Innovation Summary
Innovation Overview
The overuse and misuse of medicinal narcotics pose threats at the national and international levels. To address this issue, the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) is the first in the world to implement and operate a program that not only monitors medicinal narcotics for prescriptions and preparation in real-time but also sends warning letters and even takes administrative actions to constant violators after an in-depth review by an expert council.
However, to effectively control narcotic overuse and misuse cases in Korea, MFDS incorporated three elements into its Vigilance program: 1) Establishment of a ‘system’ that collects information throughout the entire life cycle of narcotics. 2) Establishment of ‘criteria’ that distinguish the safe use of narcotics from misuse and overuse. 3) Development of a ‘platform’ that selectively surveils the latest narcotic overuse and misuse cases.
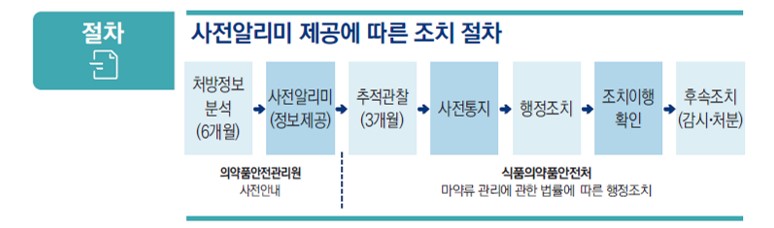
First, MFDS launched the development of a system called the Narcotics Information Management System (NIMS), which is specialized system to collect all information regarding nationwide medicinal narcotic handling: from import, manufacture, purchase, sale, and use to disposal. The extensive coverage of NIMS enables MFDS to track, trace, and analyze doctors’ peculiar patterns of prescription for their patients in real-time.
Second, MFDS established criteria for the safe management and Public Notice for misuse and overuse of narcotics (Narcotic drugs, e.g., fentanyl patch, and Psychotropic drugs, e.g., zolpidem) with an advisory committee of private sector experts from various fields, including the Korea Medical Association (KMA). The distribution of criteria for the safe use of narcotic drugs in the form of guidelines was effective in raising public awareness about the legitimate use of medicinal narcotics.
Third, MFDS developed and implemented the ‘Pre-Notification Program (PNP)’ as a stringent control platform that proactively monitors anomalies in prescription data from NIMS and evaluates suspected narcotic overuse and misuse cases based on the aforementioned criteria. To avoid hampering patients' access to their legitimate medications, PNP incorporates appeal stages both before and after the pre-notice stage for medical practitioners who failed to meet the criteria.
As a result, this innovative ‘Digitalized Real-Time Narcotics Vigilance Project’ is expected to protect public health from narcotic overuse and misuse by doctors’ mal-prescriptions. In fact, we conducted a full-fledged implementation of this project from 2022 to 2023 on three types of narcotics (propofol, zolpidem, anorectics like phentermine) and found approximately a 99% reduction, respectively. We plan to implement a fully computerized doctor notification program by 2024.
Innovation Description
What Makes Your Project Innovative?
In line with the national digitalization policy, this project utilizes digital technology to manage the entire lifecycle of narcotics, aiming to ensure the safe use of medicinal narcotics and prevent narcotics overuse and misuse.
1. MFDS implemented a distinctive system that collects the entire lifecycle of narcotics to ensure reliable tracking and tracing, as well as the analysis of doctors’ mal-prescription patterns.
2. MFDS established criteria for safe management and issued a Public Notice regarding the misuse and overuse of narcotics with input from private sector experts. These criteria serve as baselines for the consistent analysis of narcotics prescription data.
3. MFDS implemented the PNP to proactively monitor anomalies in prescription data and provide written warnings to those who fail to meet standard measures for narcotic overuse and misuse. The PNP not only increases doctors’ awareness but also that of patients regarding proper use.
What is the current status of your innovation?
The Digitalized Real-Time Narcotics Vigilance project has just completed its first round of implementation. There are ongoing successful improvements:
1. We are currently identifying limitations of traditional enforcement approaches within the regulatory criteria for reducing the misuse and overuse of medical narcotics.
2. We are upgrading relevant methods by embracing cutting-edge technologies in advanced data analytics, automatically extracting suspected cases that exceed narcotics safe use criteria.
3. We inform and notify healthcare professionals about cases involving illegal use, overuse, patient-specific doctor shopping, and their previous abuse history.
4. We continuously hold expert council meetings to review suspected cases of the non-medical use of medicinal narcotics.
Innovation Development
Collaborations & Partnerships
1. We conduct meetings with a consulting body of experts from various fields, including KMA and other related associations from the private sector.
2. We collaborated closely with the Korea Institute of Drug Safety & Risk Management (KIDS) and KMA in the development of NIMS.
3. We collaborate with the Korea Prosecution Service and the Korean National Police Agency in requesting investigations related to narcotics crimes and conducting joint inspections of narcotics abuse suspects.
Users, Stakeholders & Beneficiaries
1. All narcotics handlers are stakeholders in the Digitalized Real-Time Narcotics Vigilance project, as they are obliged to report to NIMS.
2. Through the implementation of the Digitalized Real-Time Narcotics Vigilance project, both doctors and pharmacists are encouraged to comply with the criteria for the safe use of narcotic drugs.
Innovation Reflections
Results, Outcomes & Impacts
(Result) Nine different guidelines for the safe use of narcotics have been released to stakeholders to increase awareness regarding the legitimate and illegitimate use of medicinal narcotics.
(Outcome) MFDS conducted one round of PNP for anorectics like phentermine, propofol, and zolpidem since implementation. By the end of PNP, 99% of doctors who initially failed to meet the criteria and entered the program have withdrawn from mal-prescribing practices; 1% of doctors were penalized in the form of administrative disposition.
(Impact) KMA and Korean society have formed a consensus in reducing medicinal narcotics overuse and misuse.
Challenges and Failures
MFDS has organized numerous roundtable meetings for system users in the private sector to gather comments, conduct policy briefing sessions, and take various steps to promote the utilization of the NIMS by different stakeholders. To respect the right to make a doctor’s medical treatment, including prescription medications, and incorporate experts’ advice on difficult issues, we actively seek feedback from a consulting body of experts from various fields.
Conditions for Success
The concerted effort made by relevant institutions with MFDS was a crucial aspect of success. The cooperation of KIDS in developing the relevant legal framework and NIMS, which consistently collects and shares transparent information with the surveillance team, the collaboration of the expert council and KMA, providing invaluable services in reviewing suspected narcotics abuse cases, and the assistance from local government officials for joint inspections and follow-up administrative actions all contributed to preventing narcotics overuse and misuse.
Replication
United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime has recognized the effectiveness of NIMS in preventing drug abuse in 2023, and has requested the implementation of NIMS as a foreign aid project in other countries (starting with Thailand) that need systematic narcotics management.
Lessons Learned
After conducting an analysis of narcotics overuse and misuse cases and administrative disposition of mal-prescribers, we learned a valuable lesson: when doctors and government officials pay close attention to narcotics-related issues, they can reduce patient’s overuse and misuse. This implies that to effectively prevent medicinal narcotics-related addictions, mutual interest and participation from the government, healthcare providers, and patients are essential.
Status:
- Implementation - making the innovation happen
- Evaluation - understanding whether the innovative initiative has delivered what was needed
Date Published:
28 June 2024