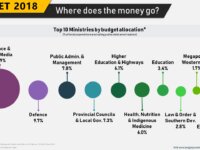
Case Study
Digital tools to monitor and predict risks in auditing Ukraine’s revolutionary online public…
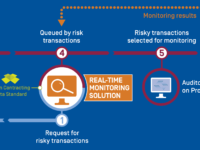
Ukraine is transforming its public procurement system to bring public procurement into the open, so citizens get a better deal and government runs smoothly. EBRD has supported the Ukrainian government to develop a new legal framework, and to develop cutting edge tools which can process vast amounts of procurement data in real time. State auditors can now quickly & pre-emptively spot risks or inefficiencies in the system and address them. It is the first innovation of this kind in the world.