Country: United States
Case Study
The Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA), a component of the United States’ Federal Government, has fully reimagined its DisasterAssistance.gov website to make applying for disaster assistance faster than ever. This change will reduce time burdens for survivors post-disaster, when they are in greatest need and the most overwhelmed. This effort has been built on decades of feedback from disaster survivors and is expected to reduce the registration time by more than 15%.
In the U.S. government, community members have experimented with designing the government services they will use. Their lived experience improves service outcomes, builds better relations with the government, and creates greater ownership over the service. This is new; normal participatory design of government services just includes community members for certain activities at certain points, never throughout, and never allowing the community to lead and frame the project or choose methodologies.
The City of Austin launched Data Impact Visuals & Exploration (DIVE) to address low data literacy, limited accessibility, and lack of decision support tools. This project aims to empower diverse users with data skills, tools, and resources to make informed decisions. DIVE benefits community members, City staff, universities and funders. Innovative features include user-centric design, multiple components, a community-based approach and a long-term sustainability plan.
The City of Austin has piloted an anticipatory governance tool named the Civic Research Agenda (CRA) to help the City become future-ready in the face of complex civic challenges.
The CRA leverages a strategic foresight methodology to proactively plan for plausible future scenarios and identify implications for decision-making today, thus moving the City away from reactionary and short-sighted policy making and enable it to “look around the corner” to future challenges and opportunities.
An ever-increasing number of AI ethicists can enumerate the most prominent risks; yet startlingly few psychologists, or other experts in behavioral science, are working on the project of aligning AI outcomes with fundamental ethical and safety principles. This knowledge gap is striking given the extraordinary investments being channeled into the technology’s ability to master and influence human behavior. In neglecting more than a century of relevant behavioral research, the ethical AI…
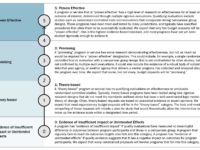
Governments must judge hundreds of new programmatic budget proposals each fiscal year with little objective information about whether they will achieve the results claimed. Evidence of program effectiveness is a critical data point that is used when making budget and policy decisions, as programs with greater evidentiary support are generally more likely to deliver a high return on investment of public funds. The The Policy Lab at Brown University leveraged existing public clearinghouses of peer…