"Påkobla Hjelpemiddel" (PH) is a digital solution developed from a digitalization department in Kristiansund Municipality, Norway. This innovative system addresses challenges in inventory, distribution, and logistics, improving the efficiency of delivering assistive devices. PH will be completed as a system in the end of 2024, but is today used by four municipalities that are a part of the innovation.
Innovation Tag: Evaluation and Oversight
Case Study
Digitalized Real-Time Narcotics Vigilance: Agile Monitoring & Pre-notification Surveillance of…
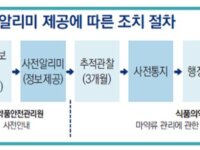
As the overuse and misuse of narcotics pose a global public health threat, the Korean governance has developed a smart, digitalized real-time monitoring system for narcotics safety management. By utilizing this state-of-the-art technology, the government can analyze prescriptions, track patterns, and alert doctors to prevent the overuse and misuse of narcotics.
The SMART LIDAR System uses advanced scanning lidar technology to monitor air quality in real-time and detect pollutants accurately. It helps identify and enforce against illegal emissions, reducing environmental pollution. Affordable and scalable, it offers an innovative solution for air quality monitoring.
The Sola calculation tool allows estimate the economic impact of 25 distinct social phenomena at municipal, regional and national level. Impact assessments at one, five and ten year intervals can lead decision-makers to better understand how to invest in wellbeing and accelerate impact investing. Results of the tool have been used in several municipalities as part of health and wellbeing promotion. A MOOC course has been developed and similar calculation tools are recently being used in other…
Case Study
Trusted Official Statistics for Good Governance and Evidence Based Decision Making in Vanuatu

The Parliament of Vanuatu has struggled to fulfil its legislative, budget, oversight, and representation functions due to limited capacity to utilise trusted statistics. The Vanuatu Bureau of Statistics addressed this capacity gap through targeted training with Members of Parliament (MPs) and parliamentary civil servants to improve policy making. This is the first focused effort in Vanuatu to introduce data for sustainable development monitoring to MPs with the aim of enhancing good governance.
Case Study
A network-based Competence Centre for Sustainable and Innovative public procurement in Finland
The Finish Government established a network-based Competence Centre for Sustainable and Innovative Public Procurement (KEINO) in 2018. The Centre provides, free of charge, advisory services to public procurers, promotes the strategic importance of procurement competencies in public management, facilitates creation of buyers’ groups among procurers, and disseminates information and good practices. The network consists of five public organisations.
Most of the public entities only had physical complaint books and no complaint handling processes to improve services to citizens. The innovative proposal was co-created between citizens and civil servants from different entities at the national level. It contemplates a standardised digital platform as a single channel for public entities and improves the management of citizen complaints through an agile and user-friendly process focused on the citizen experience.
The Disciplinary Maturity Model (CRG-MM) is a pioneer model in Brazil and is an operational and strategic tool aimed to evaluating and improving the management of disciplinary activity, through the definition of quality standards based on management and public governance procedures. This innovation seeks to provide greater stability and security to executors and managers of disciplinary activity, considering its role as a public integrity instance in the fight against corruption.
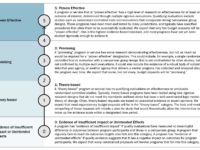
Governments must judge hundreds of new programmatic budget proposals each fiscal year with little objective information about whether they will achieve the results claimed. Evidence of program effectiveness is a critical data point that is used when making budget and policy decisions, as programs with greater evidentiary support are generally more likely to deliver a high return on investment of public funds. The The Policy Lab at Brown University leveraged existing public clearinghouses of peer…
The UK Government Policy Profession has piloted a new model called Shared Policy Capability Project to support department leaders and policy makers undertake a facilitated self-assessment of their policy environment and identify opportunities for improvement. Through this the government aims to build capability at a department level and enable policymakers to take an active role in improving the environment in which they make policy.